
 Anonymous
September 29, 2023
Anonymous
September 29, 2023
Java 8 introduced several significant features and enhancements to the Java programming language.
- Lambda Expressions ,
- Functional Interfaces ,
- Method References ,
- Stream API ,
- Default Methods ,
- New Date and Time API ,
- Nashorn JavaScript Engine ,
- Improved Collections
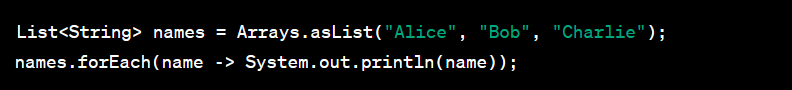
Lambda Expressions:
Lambda expressions provide a concise way to define anonymous functions (or closures) in Java. They enable functional programming constructs and make it easier to work with collections using the Streams API.
Example:
Functional Interfaces:
Functional interfaces are interfaces that have exactly one abstract method. Java 8 introduced the @FunctionalInterface annotation to help developers identify such interfaces, and they can be used effectively with lambda expressions.
Example:

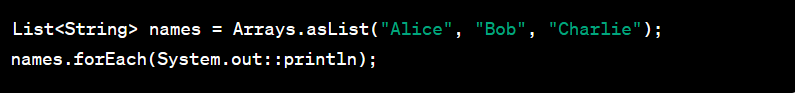
Method References:
Method references allow you to refer to methods or constructors using the :: operator. They provide a more concise way to call methods or constructors, especially in conjunction with lambda expressions.
Example:
Stream API:
The Stream API is a powerful addition for working with sequences of elements, such as collections or arrays. Streams enable functional-style operations like mapping, filtering, and reducing on data.
Example:
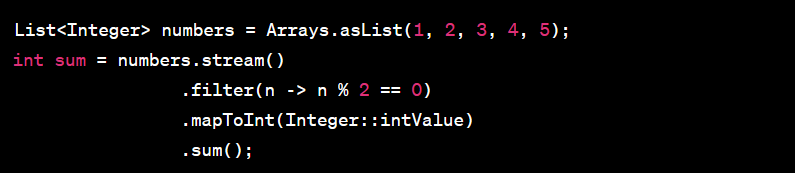
Default Methods:
Java 8 introduced the concept of default methods in interfaces. These methods have an implementation in the interface itself, allowing developers to add new methods to interfaces without breaking existing implementing classes.
Example:
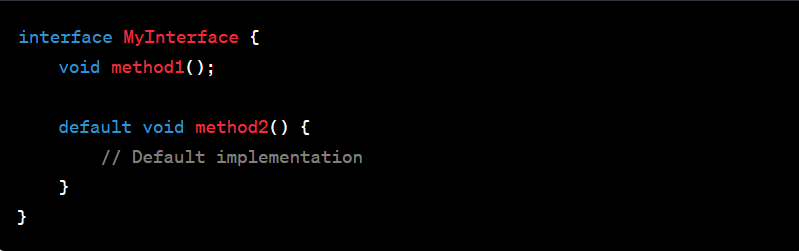
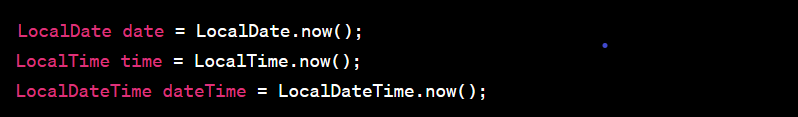
New Date and Time API:
Java 8 introduced the java.time package, which provides a modern, comprehensive date and time API. This API offers better handling of dates, times, time zones, and periods, addressing many shortcomings of the old java.util.Date and java.util.Calendar classes.
Example:
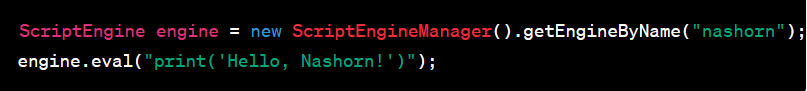
Nashorn JavaScript Engine:
Java 8 includes the Nashorn JavaScript engine, which allows you to execute JavaScript code from within Java applications. It offers improved performance and better integration with Java..
Example:
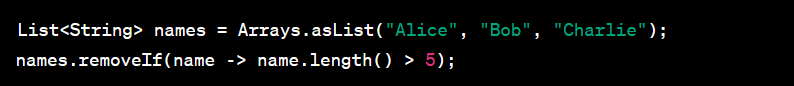
Improved Collections:
Java 8 added several new methods to the java.util.Collection interface, including forEach, removeIf, and stream, which make working with collections more convenient and efficient.
Example:
These features have made Java more expressive and flexible, enabling developers to write cleaner and more efficient code while embracing functional programming paradigms.

